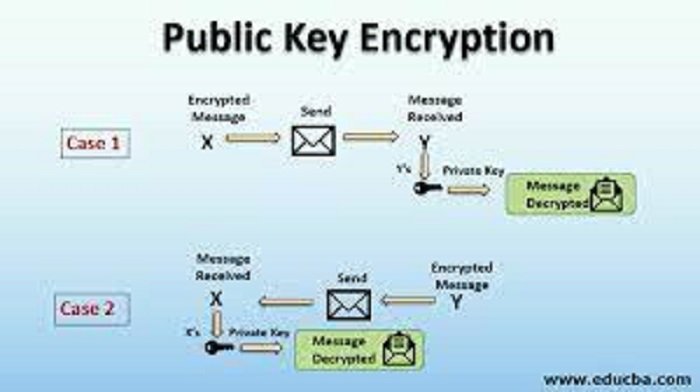
In the realm of cryptography and secure communication, public keys play a pivotal role in ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of data. This blog post explores the fundamentals of public keys, their role in asymmetric encryption, and the importance they hold in safeguarding digital communication.
The Basics of Public Key Cryptography
- Asymmetric Encryption:
Public key cryptography, also known as asymmetric encryption, involves the use of a pair of keys—a public key and a private key. These keys are mathematically linked but serve distinct purposes in the encryption and decryption processes.
- Public Key Infrastructure (PKI):
Public keys are a fundamental component of Public Key Infrastructure, a framework that manages digital keys and certificates. PKI facilitates secure communication over the internet by enabling the encryption of sensitive information.
Understanding Public Keys
- Public Key Functions:
The public key is shared openly and used for encryption by anyone who wishes to send secure information to the key’s owner. It plays a crucial role in establishing secure communication channels.
- Encryption Process:
When someone wants to send encrypted data to a recipient, they use the recipient’s public key to encrypt the information. The encrypted data can only be decrypted using the corresponding private key, which is known only to the recipient.
- Digital Signatures:
Public keys are also used to verify digital signatures. In this process, the sender uses their private key to create a unique digital signature, and the recipient uses the sender’s public key to verify the authenticity of the signature.
Security and Trust
Navigating the Crypto Landscape: Understanding ICOs (Initial Coin Offerings)
- Key Pair Generation:
Public and private key pairs are generated using complex algorithms. The security of the system relies on the computational difficulty of deriving the private key from the public key.
- Trust in Public Keys:
Trust in the security of public keys is crucial for the effectiveness of asymmetric encryption. Various mechanisms, including digital certificates issued by trusted Certificate Authorities, help establish and verify the legitimacy of public keys.
Practical Applications
- Secure Online Communication:
Public key cryptography is widely used to secure online communication, such as HTTPS connections for secure browsing, email encryption, and secure file transfer protocols.
- Digital Transactions:
Public keys play a crucial role in securing digital transactions, including online banking, e-commerce transactions, and cryptocurrency transfers. They ensure the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive financial data.
- Secure Authentication:
Public keys are integral to secure authentication processes, providing a means for users to prove their identity in secure online environments.
Conclusion
Public keys form the backbone of secure digital communication, enabling the encryption and authentication mechanisms that underpin the modern internet. As technology advances and the need for secure online interactions grows, understanding the role and significance of public keys becomes increasingly essential.
The use of public key cryptography not only safeguards sensitive information but also fosters a digital environment where trust, security, and privacy are paramount.